How to operate a drone? It’s a question many ask, leading to a fascinating journey into the world of unmanned aerial vehicles. From understanding the intricate mechanics of propellers and motors to mastering advanced flight techniques and navigating safety regulations, operating a drone successfully requires knowledge, practice, and a keen eye for detail. This guide will equip you with the essential skills and understanding to confidently take to the skies.
This comprehensive guide delves into every aspect of drone operation, starting with a detailed explanation of drone components and their functions. We’ll then cover pre-flight checks, basic and advanced flight maneuvers, safety regulations, and essential maintenance procedures. By the end, you’ll possess a solid foundation for safely and effectively piloting your own drone.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for both safe operation and effective troubleshooting. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight capabilities, and familiarity with their functions and potential failure points is essential for any drone pilot.
Drone Component Breakdown

The following table details the key components of a typical quadcopter drone, their functions, and common points of failure.
| Component | Function | Potential Failure Points |
|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Provide thrust for lift and maneuverability. | Cracks, bending, imbalance, wear and tear. |
| Motors | Rotate the propellers, generating thrust. | Burnout, overheating, damaged windings, bearing failure. |
| Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs) | Control the speed and direction of the motors. | Overheating, short circuits, malfunctioning firmware. |
| Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone; processes sensor data and controls the motors. | Software glitches, hardware failure, sensor malfunctions. |
| Battery | Provides power to all drone components. | Discharge, cell imbalance, physical damage, overheating. |
| GPS Module | Provides location data for autonomous flight and features like Return-to-Home (RTH). | Signal loss, malfunctioning receiver, interference. |
| Camera (if applicable) | Captures photos and videos. | Lens damage, sensor failure, malfunctioning image processing unit. |
| Radio Transmitter | Allows the pilot to control the drone remotely. | Low battery, signal interference, damaged antenna. |
| Receiver | Receives signals from the transmitter and relays them to the flight controller. | Signal interference, hardware failure. |
Drone Motor Types and Flight Performance, How to operate a drone
Different drone motors offer varying performance characteristics. Brushed motors are simpler and cheaper but less efficient and less powerful than brushless motors. Brushless motors, while more expensive, provide superior power, efficiency, and longer lifespan, making them the preferred choice for most drones. The choice of motor directly impacts flight time, speed, and maneuverability.
Drone Assembly Procedure
Assembling a drone involves carefully connecting each component. Begin by securely attaching the motors to the drone frame, ensuring proper alignment. Then, connect the ESCs to the motors and the flight controller. Next, connect the battery and the receiver. Finally, carefully attach the propellers, ensuring they are correctly oriented.
A visual guide showing each step would be beneficial, ensuring proper alignment and connection of each component to avoid potential damage or malfunctions.
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is essential to ensure safe and successful operation. This involves verifying the drone’s readiness and identifying any potential issues that could compromise flight safety.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning the basics is crucial for safe and effective flight, and a great resource to begin your journey is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This guide will equip you with the necessary knowledge to confidently handle your drone, ensuring both a successful and responsible flying experience.
Pre-Flight Checklist
The following checklist should be followed before every flight:
- Check battery level (ensure sufficient charge for planned flight time).
- Inspect propellers for damage (cracks, bends, or other imperfections).
- Verify GPS signal strength (a strong signal is crucial for stable flight).
- Confirm all components are securely attached.
- Calibrate the drone’s sensors (IMU, compass, etc.).
- Check radio transmitter battery level.
- Review the flight area for obstacles and potential hazards.
- Check weather conditions (avoid flying in strong winds or rain).
Sensor Calibration
Calibrating the drone’s sensors is critical for accurate flight performance. This process ensures the drone’s internal sensors (such as the IMU and barometer) are properly aligned and provide reliable data to the flight controller. Failure to calibrate can lead to erratic flight behavior.
Pre-Flight Procedure Flowchart
A flowchart visually Artikels the steps involved in the pre-flight procedure, ensuring a systematic and thorough check before takeoff. The flowchart would start with a “Start” node, proceed through each checklist item, culminating in a “Ready for Flight” or “Abort Flight” decision node.
Basic Drone Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding the basic controls is fundamental to operating a drone safely and effectively. This section Artikels the functions of the control sticks and the steps involved in basic flight maneuvers.
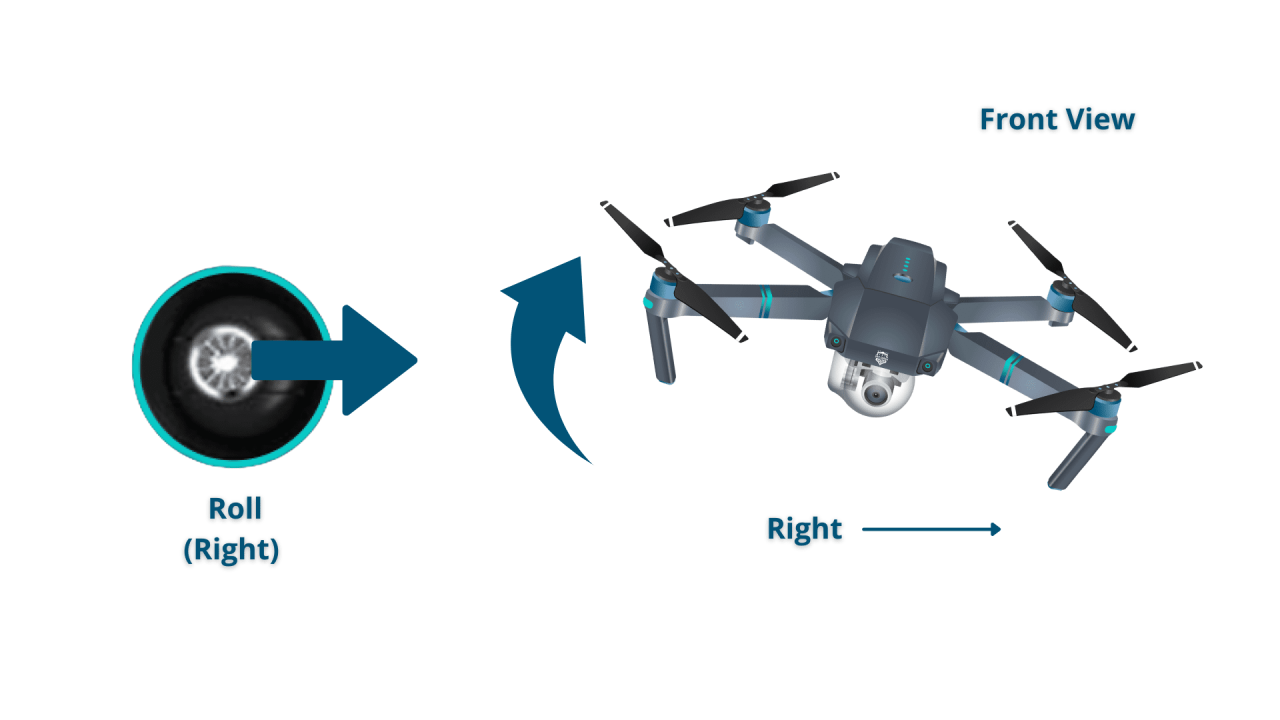
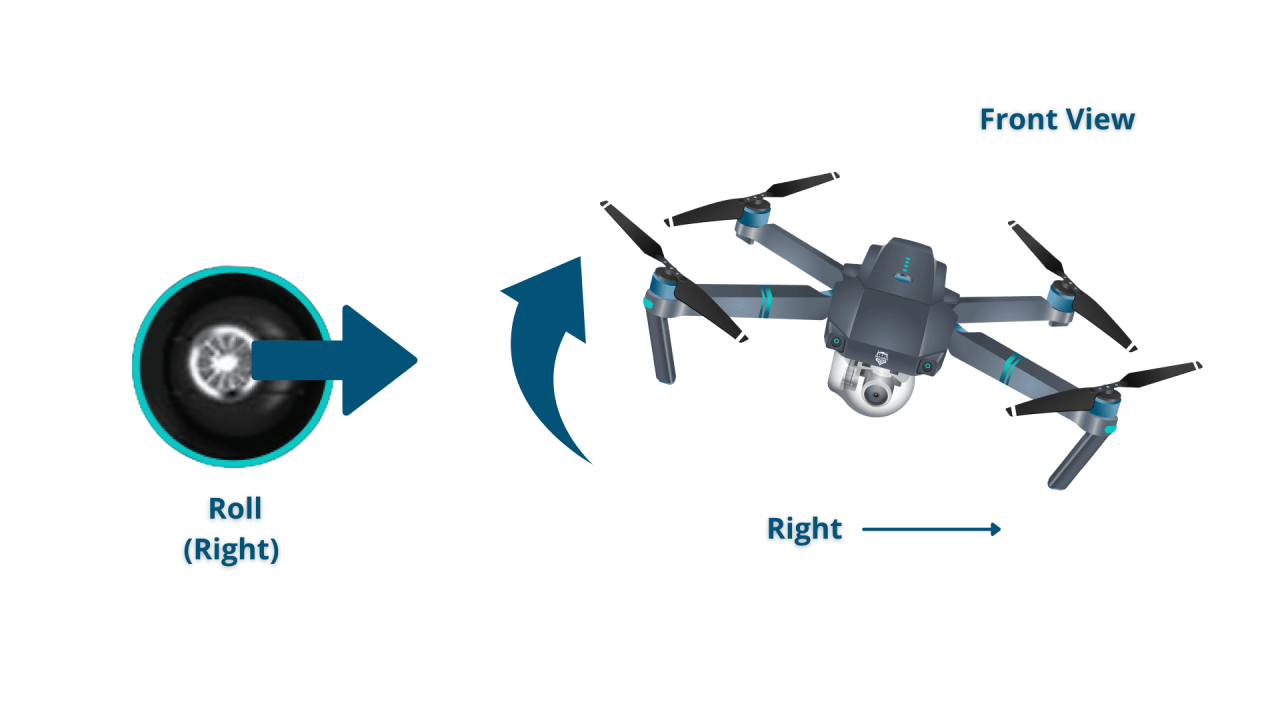
Drone Control Sticks
Most drones utilize two control sticks: one for controlling throttle and yaw, and the other for pitch and roll. The left stick typically controls throttle (up/down) and yaw (rotation), while the right stick controls pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right). A clear illustration showing the stick positions and their corresponding drone movements would be helpful.
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Taking off involves gently increasing the throttle until the drone lifts off the ground. Hovering requires maintaining a constant throttle to keep the drone at a steady altitude. Moving the drone involves using the pitch and roll controls to change its direction. Landing involves gradually decreasing the throttle until the drone gently touches down.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering controls. Successfully navigating this process requires understanding regulations and practicing safe flight procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including legal considerations and practical tips, you should check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. This will ensure you’re well-prepared and can fly safely and responsibly.
Drone Control Modes
Different drone control modes cater to pilots of varying skill levels. Beginner mode often restricts the drone’s speed and maneuverability, while expert mode offers full control, allowing for more complex flight maneuvers. The selection of mode should align with the pilot’s experience and the complexity of the intended flight.
Advanced Drone Flight Techniques
Once comfortable with basic flight, pilots can explore more advanced techniques to enhance their aerial photography and videography skills and overcome challenges like windy conditions.
Aerial Photography and Videography
Smooth camera movements are crucial for high-quality aerial footage. Techniques such as adjusting the camera angle, using smooth joystick movements, and employing features like gimbal stabilization can significantly improve the quality of the captured content. A detailed explanation of how to achieve smooth, cinematic shots would be invaluable.
Flying in Windy Conditions
Wind significantly impacts drone stability and control. Pilots need to adjust their flight technique, potentially reducing speed and using more precise control inputs. Employing features like wind compensation (if available) can help mitigate the effects of wind. Understanding wind patterns and adjusting flight plans accordingly is essential for safe operation in windy environments.
Performing a 360-Degree Aerial Shot
A 360-degree aerial shot involves smoothly rotating the drone around a central point to capture a complete panoramic view. This requires precise control of the yaw axis, ensuring a steady and consistent rotation speed. A step-by-step guide on achieving a smooth and visually appealing 360-degree shot would be beneficial.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Adhering to safety regulations and best practices is paramount for responsible drone operation. This includes understanding airspace restrictions and maintaining a safe distance from people and obstacles.
Drone Safety Regulations
| Regulation Type | Description | Consequences of Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Airspace Restrictions | Restrictions on flying near airports, military bases, and other sensitive areas. | Fines, legal action, drone confiscation. |
| Registration Requirements | Requirements for registering drones with relevant authorities. | Fines, legal action. |
| Flight Restrictions | Limitations on flight altitude, distance from the operator, and flight time. | Fines, legal action. |
| Privacy Concerns | Restrictions on flying over private property without permission. | Legal action, civil lawsuits. |
Safe Operating Procedures

Maintaining a safe distance from people and obstacles is crucial to prevent accidents. Always be aware of your surroundings and avoid flying in crowded areas or near power lines. Understanding the limitations of your drone and respecting the privacy of others is essential.
Reporting Drone Accidents or Malfunctions
In case of an accident or malfunction, immediately report the incident to the relevant authorities. Documenting the event, including the date, time, location, and any potential causes, is important for investigation and future safety improvements.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its continued reliable performance. This section Artikels a maintenance schedule and troubleshooting steps for common issues.
Drone Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule helps to prevent potential problems and ensure the drone’s longevity. This schedule should include tasks such as cleaning propellers, inspecting the battery, checking for loose screws, and visually inspecting the drone for any signs of damage. A detailed maintenance schedule with recommended frequency for each task would be beneficial.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
The following steps can be used to troubleshoot some common drone problems:
- Motor Failure: Check motor connections, ESC functionality, and battery voltage. Replace damaged components as needed.
- GPS Signal Loss: Ensure clear skies and unobstructed GPS signal. Recalibrate the GPS module.
- Low Battery Warning: Land the drone immediately and recharge the battery. Avoid flying until the battery is fully charged.
- Flight Controller Malfunction: Try recalibrating the sensors. If the problem persists, contact the manufacturer for support or repair.
- Propeller Damage: Replace damaged propellers immediately. Ensure the replacement propellers are correctly sized and oriented.
Replacing Damaged Drone Components
Replacing damaged components requires careful attention to detail. Ensure that replacement parts are compatible with your drone model. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully to avoid further damage or malfunction. A step-by-step guide with visual aids would be beneficial for each component replacement procedure.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding experience, opening up a world of possibilities for photography, videography, and exploration. Remember that safety and adherence to regulations are paramount. By diligently following the steps Artikeld in this guide and continuously practicing, you’ll be well-prepared to navigate the skies responsibly and enjoy the incredible capabilities of your drone. Safe flying!
Common Queries: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
For beginners, a ready-to-fly drone with GPS stabilization and beginner-friendly flight modes is recommended. Look for models with features like automatic return-to-home.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, size, and flight conditions. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes of flight time on a single charge.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
If you lose control, immediately attempt to engage the return-to-home function (if available). If that fails, try to land it manually or contact local authorities if it poses a safety risk.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific regulations and registration procedures.